Understanding sperm production and release is crucial for grasping male reproductive health. This post explores how many sperm men typically store, how many are released during ejaculation, and factors that can influence sperm count and quality.
1. How Many Sperm Do Men Produce?
1.1. Sperm Production Rates
Men continuously produce sperm throughout their lives. On average:
- Daily Production: A healthy man produces approximately 1,500 to 3,000 sperm per second, which equates to about 100 million to 300 million sperm per day.
- Total Sperm Count: Over a lifetime, a man can produce billions of sperm.
1.2. Spermatogenesis
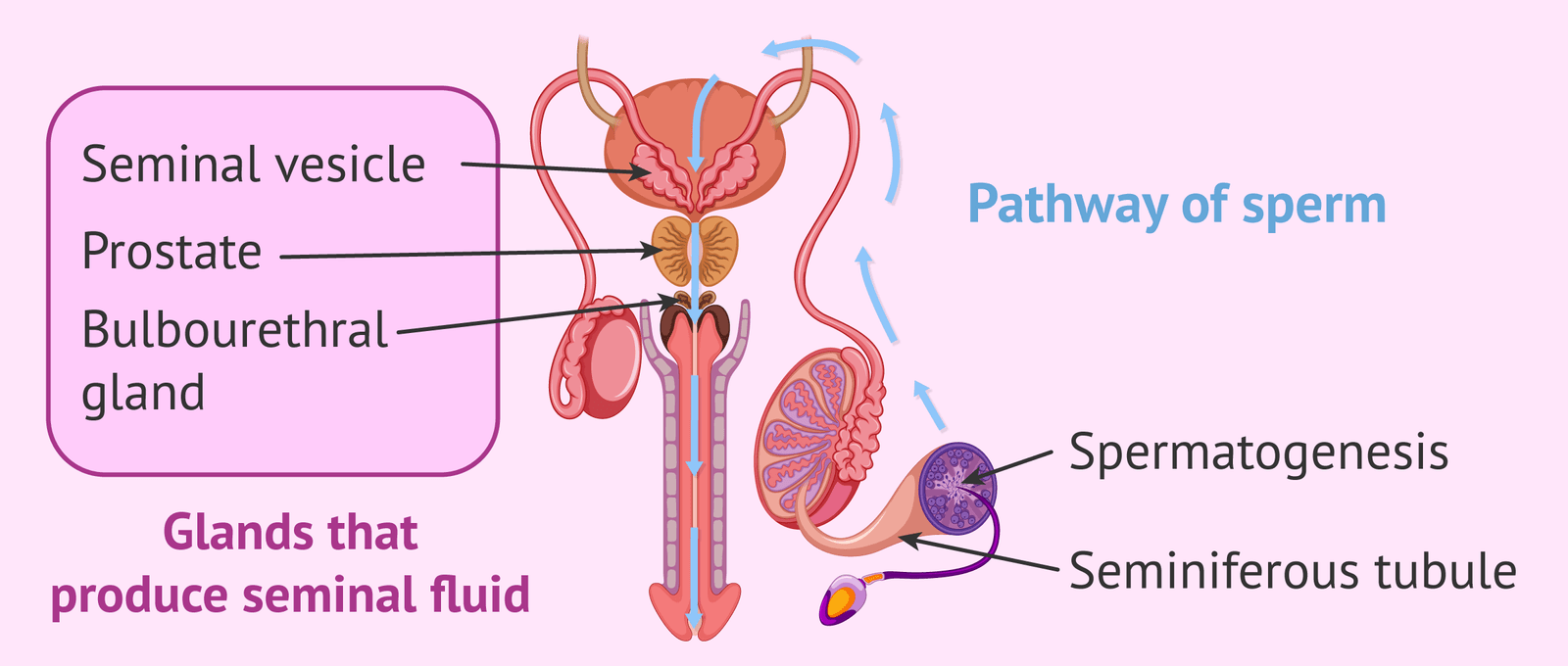
Sperm production occurs in the testes through a process called spermatogenesis:
- Duration: Spermatogenesis takes about 64 to 72 days to complete.
- Continuous Process: Sperm production is ongoing, with mature sperm being stored in the epididymis until ejaculation.
2. How Many Sperm Are Released at Once?
2.1. Ejaculation Volume and Sperm Count
During ejaculation, the average volume of semen is about 2 to 5 milliliters (ml), which contains:
- Sperm Count per Ejaculation: Typically, between 40 million to 300 million sperm per milliliter of semen are released. Therefore, each ejaculation can contain anywhere from 80 million to 1.5 billion sperm.
- Factors Affecting Sperm Count: The sperm count can be influenced by various factors, including age, health, lifestyle, and frequency of ejaculation.
2.2. Sperm Concentration and Quality
Sperm concentration and quality are important for fertility:
- Normal Range: The World Health Organization (WHO) defines a normal sperm concentration as at least 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen.
- Sperm Health: Factors such as motility (movement), morphology (shape), and overall sperm health play a role in reproductive success.
Exploring Digital Opportunities
In today’s fast-paced digital world, finding engaging platforms adds variety to everyday life. Websites such as casinoviplogin.com provide interactive experiences that complement both work and leisure. Just as communities thrive on collaboration and growth, exploring diverse online spaces can enhance balance and creativity. This blend of information and entertainment keeps users inspired and connected.
3. Factors Influencing Sperm Production and Release
3.1. Health and Lifestyle
Several factors can impact sperm production and release:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports healthy sperm production.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity contributes to overall reproductive health.
- Lifestyle Choices: Avoiding smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can help maintain optimal sperm production.
3.2. Environmental and Medical Factors
Environmental and medical factors can also affect sperm count:
- Exposure to Toxins: Exposure to environmental toxins and chemicals can negatively impact sperm production.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as varicocele, hormonal imbalances, and infections can affect sperm production and quality.
3.3. Age
Age can influence sperm production:
- Decreased Production: Sperm production and quality may decrease with age, typically after the age of 40.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic abnormalities may also become more prevalent with age.
4. Maintaining Healthy Sperm Production
4.1. Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups can help identify and address any potential issues with sperm production:
- Fertility Assessments: Men experiencing fertility issues should consider a fertility assessment to evaluate sperm count and quality.
- Professional Guidance: Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice on maintaining reproductive health.
4.2. Healthy Habits
Adopting healthy habits supports sperm production:
- Balanced Diet: Include foods rich in antioxidants, zinc, and vitamins C and E.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated to support overall health and sperm production.
- Stress Management: Manage stress through relaxation techniques and healthy coping mechanisms.
Conclusion
Men produce a significant number of sperm daily, with millions released during each ejaculation. Understanding the factors influencing sperm production and release can help maintain reproductive health and address potential concerns. By adopting healthy habits and seeking professional advice, men can support optimal sperm production and overall reproductive well-being.





